Understanding Double Wall Framing and Code Compliance
Double wall framing is an advanced construction method used to improve energy efficiency by increasing the insulation value (R-value) of walls beyond standard single stud walls. While double stud wall wood framing is not explicitly addressed in the International Residential Code (IRC) or International Energy Conservation Code (IECC), it is becoming a preferred method in high-performance and energy-efficient homes. This blog outlines key considerations for ensuring compliance with applicable codes and provides best practices for design, plan review, and field inspections of double wall framing systems.
Benefits of Double Wall Framing
Higher R-Value for Enhanced Energy Efficiency
The primary benefit of double wall framing is its ability to achieve significantly higher insulation values compared to traditional single stud walls. For example:
- Standard single stud wall: Typically achieves an R-value of R-19 (2×6 wall) or R-20 with cavity insulation.
- Double wall framing: Can achieve R-values of R-30 or higher, depending on cavity depth and insulation type.
This increase in thermal resistance reduces heat transfer, leading to improved energy efficiency and lower utility bills.
Code Compliance Challenges for Double Wall Framing
Insulation Requirements
Although the IRC and IECC specify minimum R-values based on single stud walls, double wall framing often exceeds these requirements. For example:
- In Climate Zone 5, the IECC mandates a minimum of R-20 cavity insulation or R-13 cavity insulation plus R-5 continuous insulation.
- Double wall systems typically exceed these values by providing R-30 to R-40 insulation, meeting or exceeding prescriptive compliance pathways.
Plan Review for Insulation Compliance
When reviewing plans involving double wall framing:
- Ensure accurate R-value calculations: Verify that the R-values are correctly calculated and documented.
- Compliance method: Confirm whether compliance is achieved prescriptively, through trade-offs, or via performance-based modeling.
- Alignment with thermal envelope requirements: Ensure the insulation is in continuous alignment with the air barrier, per IECC Section R402.4.
Moisture Control Considerations
Moisture control is critical in double wall construction to prevent condensation and long-term structural damage. The placement of vapor retarders depends on climate zones and IRC requirements.
Placement of Vapor Retarders
The 2012 IRC Section 702.7 specifies that vapor retarders are required in colder climates (Zones 5-8). Recommendations include:
- Location of vapor retarder: Install the vapor retarder on the exterior side of the interior wall.
- Class of vapor retarder: Depending on the climate zone, Class I, II, or III vapor retarders may be used.
IRC Definitions of Vapor Retarder Classes
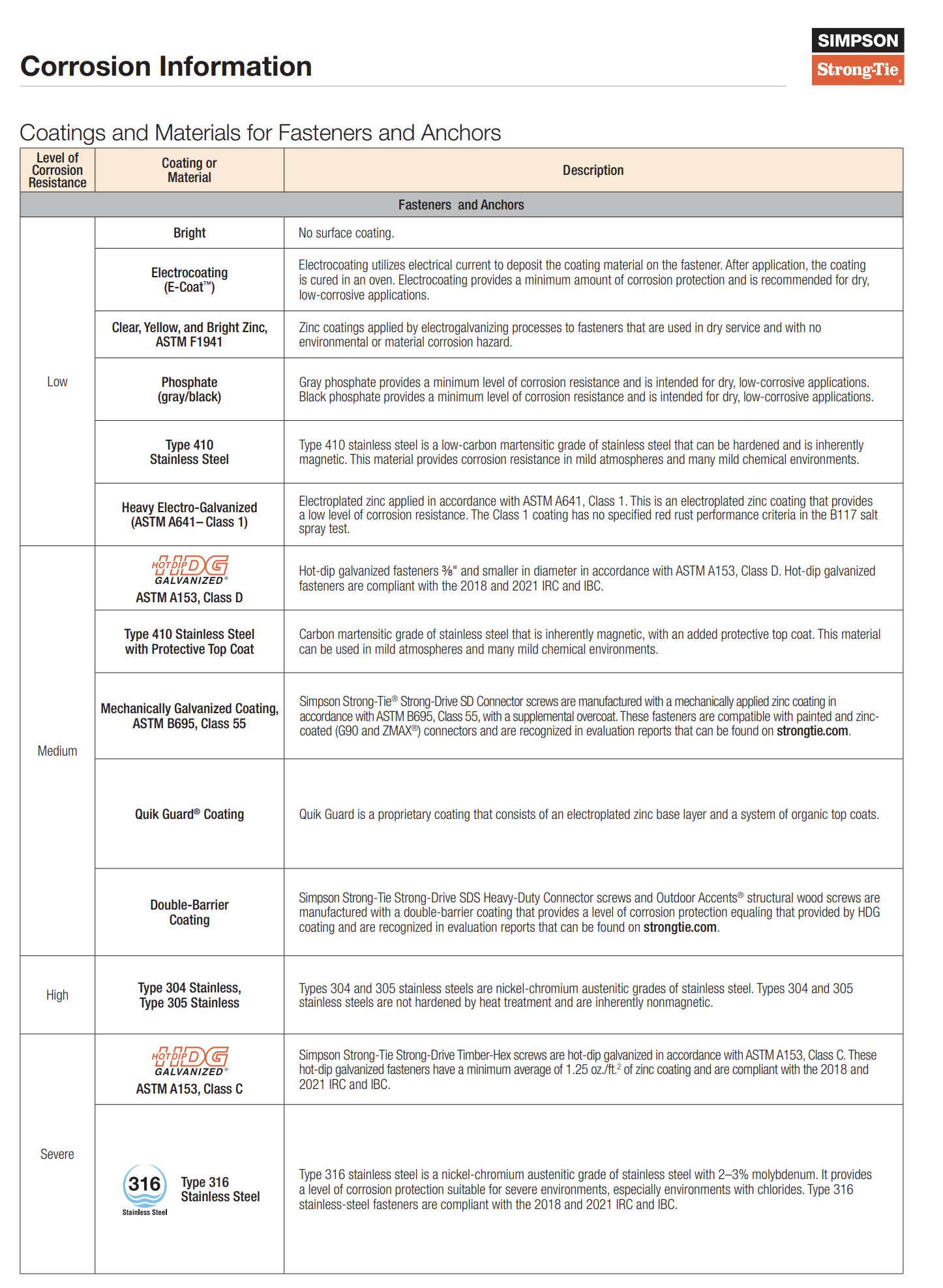
- Class I: Sheet polyethylene or unperforated aluminum foil.
- Class II: Kraft-faced fiberglass batts.
- Class III: Latex or enamel paint.
Conditions for Class III Vapor Retarders
In some climates, Class III vapor retarders may be used if certain conditions are met:
- Climate Zone 5: Requires vented cladding or insulated sheathing with an R-value ≥ 5 over a 2×4 wall or ≥ 7.5 over a 2×6 wall.
- Climate Zone 6: Insulated sheathing with R-value ≥ 7.5 over a 2×4 wall or ≥ 11.25 over a 2×6 wall.
- Climate Zones 7 and 8: Require insulated sheathing with an R-value ≥ 10 over a 2×4 wall or ≥ 15 over a 2×6 wall.
Air Leakage Control
Air leakage in double wall systems can undermine the thermal performance of high R-value insulation. The IECC Table R402.4.1.1 and IRC Table N1102.4.1.1 require the installation of a continuous air barrier.
Best Practices for Air Barrier Installation
- Placement of the air barrier: Specify a continuous air barrier on the interior side of the interior wall.
- Sealing gaps and penetrations: Ensure that all seams, gaps, and holes are properly sealed, including:
- Corners and headers
- The junction of the foundation and sill plate
- The junction of the top plate and top of exterior walls
- Inspection: Inspect the air barrier during construction to confirm continuous alignment with the thermal envelope.
Field Inspection Checklist for Double Wall Framing
Insulation Installation
- Ensure that insulation completely fills the cavity without compression or gaps.
- Verify that insulation is in continuous contact with the air barrier.
Vapor Retarder Installation
- Confirm proper placement of the vapor retarder on the exterior side of the interior wall.
- Ensure insulation on both sides of the vapor retarder is fully aligned and continuous.
Air Barrier Installation
- Inspect for a continuous air barrier on the interior side of the interior wall.
- Check that all seams and gaps are properly sealed.
- Verify that the exterior thermal envelope is in substantial contact with the air barrier.
Conclusion
Double wall framing offers superior insulation and energy efficiency for residential construction but requires careful attention to moisture control, air leakage, and code compliance. Proper planning, accurate documentation, and thorough inspections are essential to ensure code-compliant installations.
For immediate service or consultation, you may contact us at Allied Emergency Services, INC.
Contact Information:
- Phone: 1-800-792-0212
- Email: Info@AlliedEmergencyServices.com
- Location: Serving Illinois, Wisconsin, and Indiana with a focus on the greater Chicago area.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. For professional advice, consult experts in the field.