Ensuring Code-Compliant Insulated Wall Intersections
Proper insulation of interior/exterior wall intersections is a critical component of energy-efficient building design. Ensuring these intersections are insulated to the same R-value as the rest of the exterior wall helps prevent thermal bridging, which can compromise the building’s thermal envelope. Builders, remodelers, and code officials must ensure that wall intersections comply with the 2015 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) and International Residential Code (IRC) standards to achieve energy efficiency, comfort, and structural integrity.
This blog outlines key considerations for ensuring that insulated interior/exterior wall intersections meet code requirements, including plan review, construction documentation, and field inspections. Following these guidelines can improve compliance, streamline inspections, and reduce costly revisions.
Why Proper Insulation of Wall Intersections Matters
Wall intersections are vulnerable to thermal bridging, where heat transfers through poorly insulated areas, leading to:
- Increased heating and cooling costs
- Condensation issues, which can cause mold and structural damage
- Reduced occupant comfort
Ensuring continuous insulation at these junctions helps maintain a consistent R-value throughout the wall assembly and meets IECC/IRC requirements for the building thermal envelope.
Plan Review Checklist for Insulated Wall Intersections
Documentation Requirements
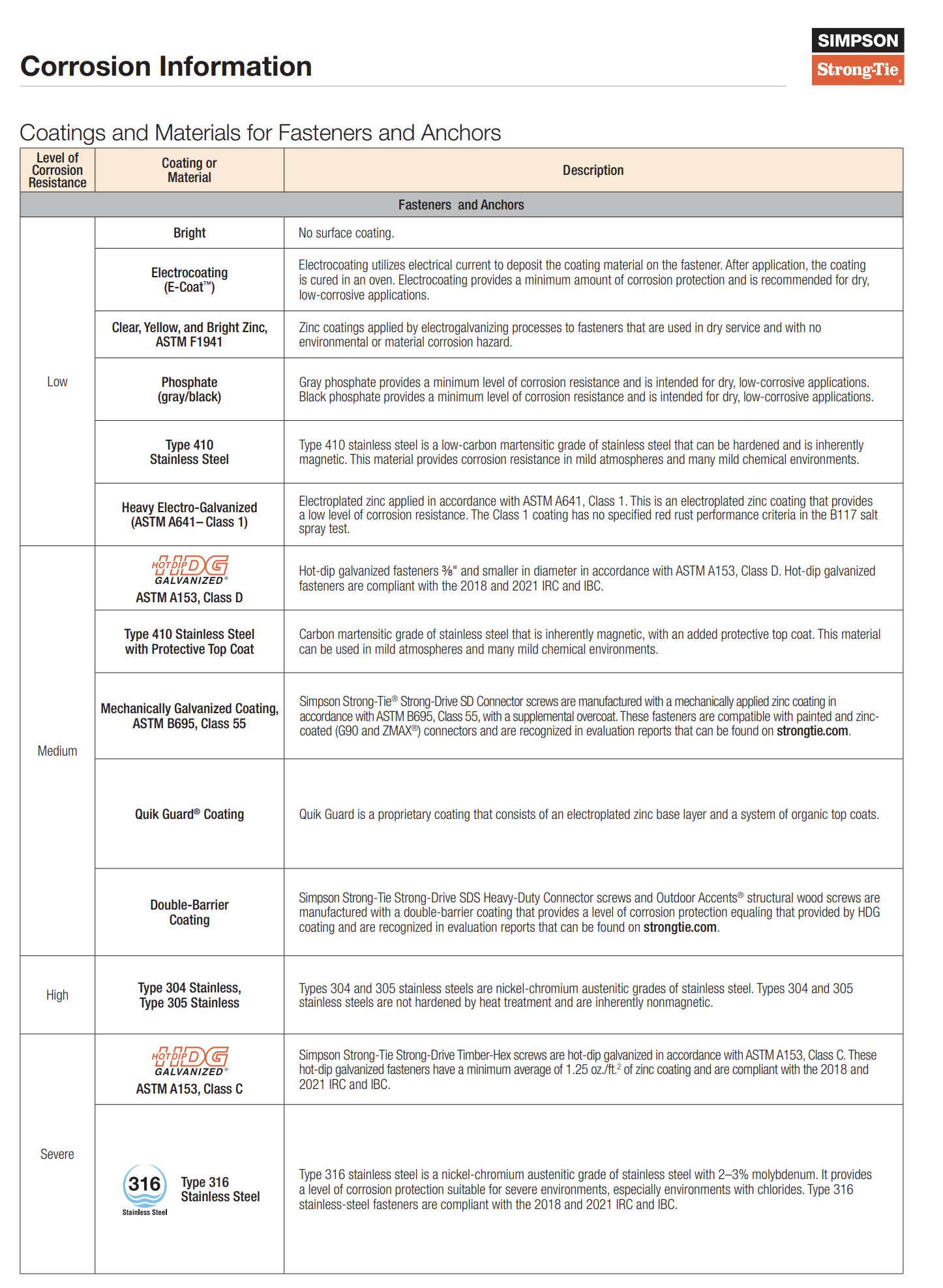
Per 2015 IECC/IRC Sections R103.3/R106.3, construction documents must be reviewed by the code official to verify compliance. The following should be included in the plans:
- Wall Compliance Approach
- Clearly indicate whether the project follows the R-value computation, U-factor alternative, or total UA alternative approach.
- Insulation Details
- Specify insulation materials, their R-values, or U-factors.
- Show details of insulation installation at wall intersections, including advanced framing techniques.
- Advanced Framing Techniques
- Indicate the use of advanced framing methods, such as:
- Ladder blocking
- Full-length 2×6 or 1×6 nailer behind the first partition stud.
- Indicate the use of advanced framing methods, such as:
Code Requirements for Insulating Wall Intersections
Prescriptive Approaches for Compliance
- R-Value Computation
- Per 2015 IECC/IRC Section R402.1.3/N1102.1.3, insulation R-values should be computed by summing layers of cavity and continuous insulation.
- Table R402.1.2/N1102.1.2 specifies minimum R-values based on climate zones.
- Example for Climate Zone 5: R-20 cavity insulation or R-13 cavity insulation + R-5 continuous insulation.
- U-Factor Alternative
- As per Section R402.1.4/N1102.1.4, assemblies can comply by achieving U-factors equal to or less than the values in Table R402.1.4/N1102.1.4.
- Example for Climate Zone 5: Maximum U-factor of 0.060.
- Total UA Alternative
- Per Section R402.1.5/N1102.1.5, compliance can be achieved by demonstrating that the total UA (sum of U-factor times assembly area) is less than or equal to the total UA calculated using prescriptive U-factors.
- This approach allows for tradeoffs, such as improving window performance to compensate for slightly lower wall insulation at intersections.
Advanced Framing Techniques for Wall Intersections
To minimize thermal bridging, the following framing techniques are recommended:
- Ladder Blocking
- Create a cavity that allows for continuous insulation behind the intersection of interior and exterior walls.
- Full-Length Nailer
- Install a full-length 2×6 or 1×6 nailer behind the first partition stud to increase the cavity size for insulation.
- Insulated Corners and Headers
- Use advanced framing methods that allow for insulation in corners and behind headers, as specified in ASHRAE Standard 90.1.
Field Inspection Guidelines for Insulated Wall Intersections
Key Inspection Points
Per 2015 IECC Section R104 and IRC Section R109, inspections should be conducted at various stages, including framing, rough-in, and final inspection. Inspectors should verify the following:
- Insulation Installation
- Confirm that insulation runs continuously behind interior/exterior wall intersections.
- Ensure insulation matches the R-value or U-factor specified in the approved construction documents.
- Advanced Framing Verification
- Verify the use of advanced framing techniques, such as ladder blocking or full-length nailers, per the approved plans.
- Check that corners and headers are insulated, and the junctions of the foundation, sill plate, and top plate are sealed.
- Air Barrier and Air Sealing
- Ensure the installation of a continuous air barrier at wall intersections, as required by IECC Section R402.4.1.1/N1102.4.1.1.
- Confirm that all joints, seams, holes, and penetrations are sealed using caulk, gaskets, or weather stripping.
- Verify that HVAC register boots and duct penetrations are sealed to prevent air leakage.
Best Practices for Insulating Wall Intersections
- Use High-Performance Insulation
- Consider using spray foam or rigid foam board insulation to achieve higher R-values and reduce air leakage.
- Seal Gaps and Cracks
- Apply caulking or spray foam sealant around wall intersections to prevent air infiltration.
- Optimize Framing Layout
- Minimize the number of studs and use wider framing intervals to increase insulation coverage.
- Consider Energy Modeling
- Use energy modeling software to evaluate the performance of different insulation strategies and ensure compliance with UA tradeoff requirements.
Conclusion
Properly insulating interior/exterior wall intersections is essential for maintaining the energy efficiency of a building’s thermal envelope. By following the guidelines set forth in the 2015 IECC/IRC, builders can ensure compliance, reduce energy costs, and improve occupant comfort. Advanced framing techniques, combined with continuous air barriers and high-performance insulation, are key to minimizing thermal bridging and achieving code compliance.
For immediate service or consultation, contact Allied Emergency Services, INC.
Contact Information:
- Phone: 1-800-792-0212
- Email: Info@AlliedEmergencyServices.com
- Location: Serving Illinois, Wisconsin, and Indiana with a focus on the greater Chicago area.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. For professional advice, consult experts in the field.