Air Sealing and Insulating Garage Walls: A Code Compliance Guide
Air sealing and insulating garage walls is essential in improving the energy efficiency of multi-family buildings and protecting occupants from harmful emissions like carbon monoxide. Proper installation ensures garage walls effectively separate unconditioned spaces from conditioned living areas, aligning with code requirements outlined in the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) and International Residential Code (IRC).
This article provides a detailed guide for builders, code officials, and designers on air-sealing and insulating garage walls to ensure compliance and improve overall building performance.
Why Air Seal and Insulate Garage Walls?
Garage walls serve as a boundary between unconditioned spaces and the home’s conditioned areas. Properly sealing and insulating these walls not only improves energy efficiency but also provides essential protection against air infiltration of vehicle emissions and other pollutants into living spaces.
Key Benefits of Air-Sealing and Insulating Garage Walls:
- Improved Energy Efficiency: Limits heat loss and reduces heating and cooling costs.
- Enhanced Indoor Air Quality: Prevents infiltration of pollutants, including carbon monoxide, from the garage.
- Comfort and Safety: Minimizes drafts, noise, and contamination from adjoining spaces, ensuring a healthier indoor environment.
Code Requirements for Air Sealing and Insulating Garage Walls
To meet building code requirements, garage walls in multi-family dwellings should follow IECC and IRC guidelines for insulation and air sealing. These standards ensure the garage space is properly separated from the building’s thermal envelope.
Applicable Code Sections:
- Construction Documentation
- IECC/IRC Section R103.2/N1101.5: Construction documents should detail insulation R-values, air-sealing techniques, and specifications for garage doors leading into conditioned spaces.
- Air Leakage Control and Building Thermal Envelope
- 2015 IECC/IRC Section R402.4/N1102.4: The thermal envelope should limit air leakage, particularly in areas where garage walls adjoin conditioned spaces.
- Air Barrier and Insulation Installation Table (R402.4.1.1/N1102.4.1.1): Outlines requirements for continuous air barriers in garage walls, floors, and ceiling areas above garages.
- Installation Standards for Air Barriers and Insulation
- Per IECC/IRC R402.4.1.1, all insulation and air barriers must be installed according to manufacturer specifications. For instance, the junctions at the foundation, sill plate, top plate, and rim joists must be sealed to prevent air infiltration.
Best Practices for Air Sealing and Insulating Garage Walls
Following best practices for air sealing and insulation installation in garage walls can enhance compliance, energy efficiency, and occupant safety.
- Install a Continuous Air Barrier
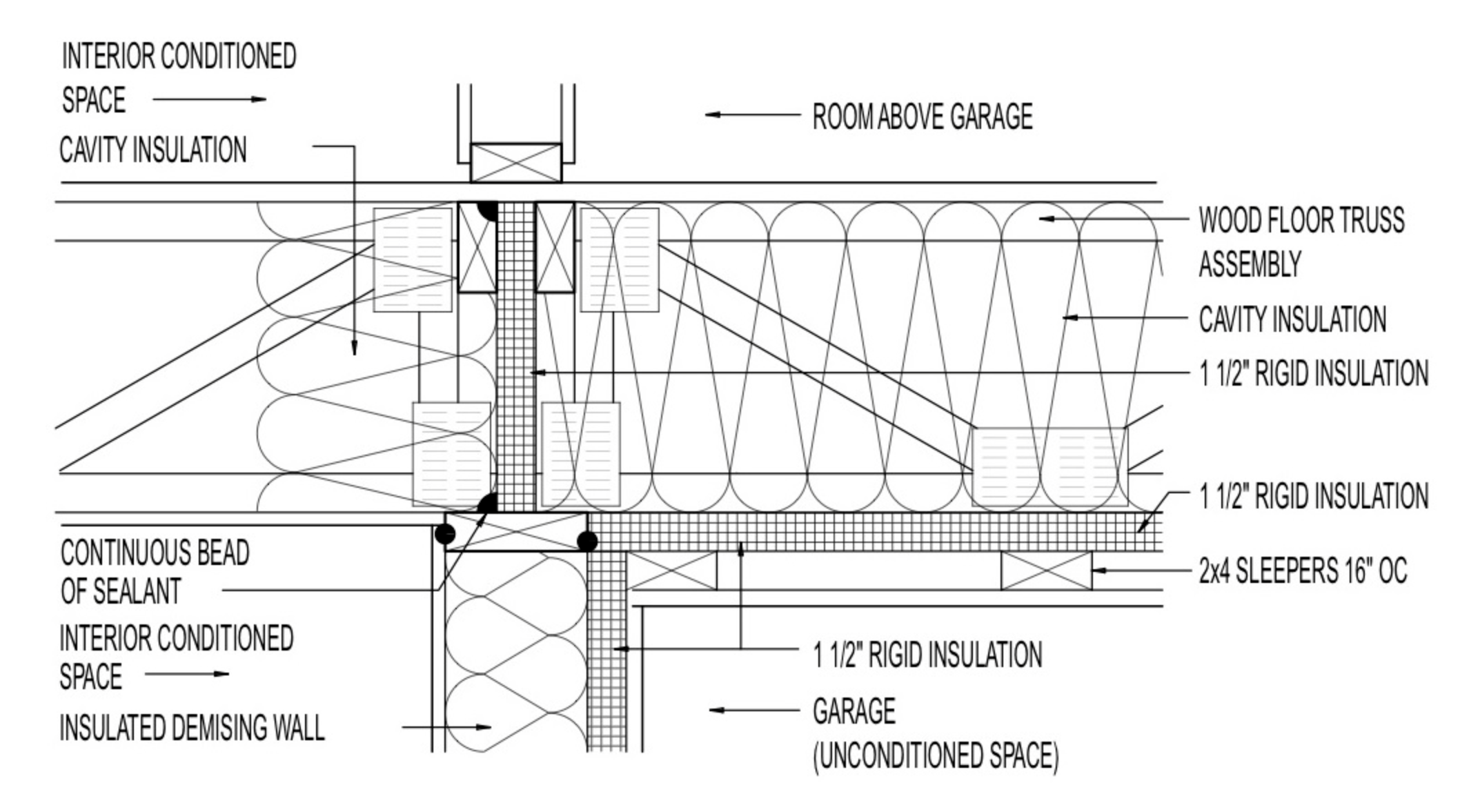
- Walls and Junctions: Seal the junctions between the foundation, sill plates, and top plates to create a continuous air barrier. This is critical to prevent any gaps that could allow air or contaminants to enter living spaces.
- Floors Above Garages: If there is living space above the garage, insulate the floor framing cavity and ensure the insulation is in contact with the subfloor. Install the air barrier along any exposed edges of insulation to prevent air leaks.
- Use High-Performance Insulation
- Wall Cavity Insulation: Choose insulation materials with an R-value appropriate for the climate zone. Rigid foam boards, for example, provide both insulation and an air barrier.
- Corners and Narrow Cavities: Fill corners and headers fully, ensuring there are no gaps. Cut insulation batts to fit narrow cavities precisely, or use a type of insulation that readily conforms to the space.
- Seal Utility Penetrations and Doorways
- Utility Penetrations: Seal around any pipes, wires, or vents that pass through garage walls into conditioned spaces. Use fire-rated sealants to maintain fire-resistance integrity.
- Garage Entry Doors: Weatherstrip doors between the garage and the home. Install thresholds and sweeps to minimize air leakage.
Plan Review Guidelines
To streamline the plan review process and ensure code compliance, construction documents should provide detailed information on air-sealing and insulation methods. According to Section R103.3/R106.3 of the IECC/IRC, the building official must review documents for code compliance.
Essential Documentation for Plan Review:
- Insulation R-Values: Ensure documents specify insulation materials and R-values in line with climate zone requirements.
- Air-Sealing Details: Include detailed methods for air sealing around utility penetrations, wall junctions, and garage entry doors.
- Manufacturer Specifications: Provide specs for doors leading from the garage to conditioned areas, including rated U-factors to confirm energy efficiency.
Inspection Protocols for Garage Walls
Field inspections are required to verify that the installation of air barriers and insulation in garage walls aligns with code requirements. According to Section R104 of the IECC and Section R109 of the IRC, all work must remain accessible for inspection until approved.
Inspection Checklist for Garage Walls:
- Verify Air Barrier Continuity: Inspect that a continuous air barrier is installed around all edges, including foundation, top plates, and any exposed insulation edges.
- Confirm Insulation Installation: Ensure wall cavities are fully insulated without gaps or compression, and that insulation is in substantial contact with the air barrier.
- Check Sealed Penetrations: Verify that all penetrations, such as wiring and pipes, are sealed to prevent air leaks and maintain fire resistance.
- Door and Threshold Inspection: Confirm that doors between the garage and living spaces have weatherstripping, and check for proper installation of thresholds and door sweeps.
Additional Considerations for Existing Buildings
For remodels and retrofits, the 2015 IECC/IRC outlines specific requirements for additions and alterations to ensure they meet code standards without affecting unaltered parts of the building.
- Additions with Attached Garages: For new additions, garage walls must follow the same air-sealing and insulation standards as new construction. Unaltered areas are generally exempt from new code requirements.
- Alterations: If wall cavities are exposed, fill them with insulation per code requirements. Ensure air-sealing techniques meet current standards, especially around doorways and utility penetrations.
Conclusion
Properly air sealing and insulating garage walls is essential for improving energy efficiency and maintaining safe indoor air quality in multi-family buildings. By following code requirements and best practices for air sealing and insulation, builders and remodelers can achieve compliance, reduce energy costs, and protect occupants from potential contaminants.
For immediate service or consultation, you may contact us at Allied Emergency Services, INC.
Contact Information:
- Phone: 1-800-792-0212
- Email: Info@AlliedEmergencyServices.com
- Location: Serving Illinois, Wisconsin, and Indiana with a focus on the greater Chicago area.
If you require immediate assistance or have specific questions, our human support is readily available to help you.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. For professional advice, consult experts in the field.